Last updated on February 6, 2025
The Role of RADIUS in Network Security
The Persistence of RADIUS/UDP and MD5

The Blast-RADIUS Attack: Exploiting MD5 Weaknesses
How the Blast-RADIUS Attack Works
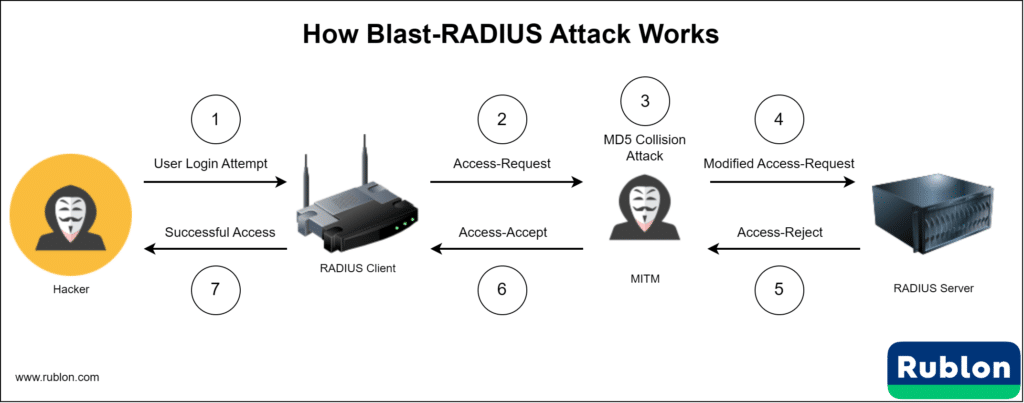
- User Login Attempt: An attacker enters a privileged user’s username and an incorrect password.
- Access-Request: The network device generates an Access-Request, including a random value called the Request Authenticator.
- MD5 Collision Attack: The attacker predicts the server’s response (an Access-Reject) and computes an MD5 collision between the predicted Access-Reject and an Access-Accept. This results in gibberish strings.
- Modified Access-Request: The attacker adds gibberish to the Access-Request disguised as a Proxy-State attribute.
- Server Responds with Access-Reject: The server checks the password, rejects the request, and sends an Access-Reject with the gibberish attached. It also computes a Response Authenticator.
- Adversary’s Swap: The attacker replaces the Access-Reject with the gibberish-filled Access-Accept and sends it to the client.
- Successful Access: Due to the MD5 collision, the client accepts the forged Access-Accept, granting the attacker access.
Blast-RADIUS Vulnerability: Assessing Feasibility and Implications
Mitigation Strategies
- Implement RADIUS over TLS: Using Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt RADIUS traffic can protect against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. RADIUS over TLS (RadSec) provides a secure, encrypted channel for transmitting authentication data. All Access-Request packets must be sent over RADIUS/TLS (RadSec).
- Use EAP RADIUS: Even though EAP-TLS sends traffic over UDP, it is still to be proven that EAP-TLS is vulnerable to the Blast-RADIUS vulnerability. However, some implementations of EAP-TLS may nevertheless be vulnerable to some variant of the Blast-RADIUS cyberattack. For that reason, it is better to use RadSec instead of EAP-TLS whenever possible.
- Deploy IPsec for Network Traffic: Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) can be used to secure communication between RADIUS clients and servers. IPsec provides authentication, integrity, and encryption, ensuring tunneled data is harder to intercept and tamper with during transit. Even though IPsec makes it harder for the attacker to access the network traffic, it is still better to use RadSec.
- Enforce MFA With Message-Authenticator Support (via Rublon Authentication Proxy 3.5.3+): RADIUS integrations can mitigate Blast-RADIUS by enforcing validation of the Message-Authenticator attribute. An MFA provider must support this attribute and allow enforcing it to safeguard against Blast-RADIUS attacks. In Rublon Authentication Proxy version 3.5.3 and newer, the force_message_authenticator option (enabled by default) secures RADIUS traffic against forged Access-Accept packets. You can learn more in the Rublon Authentication Proxy documentation.