Last updated on February 21, 2025
Start Free Trial
No Credit Card Required
PAP vs. CHAP: What’s the Difference?
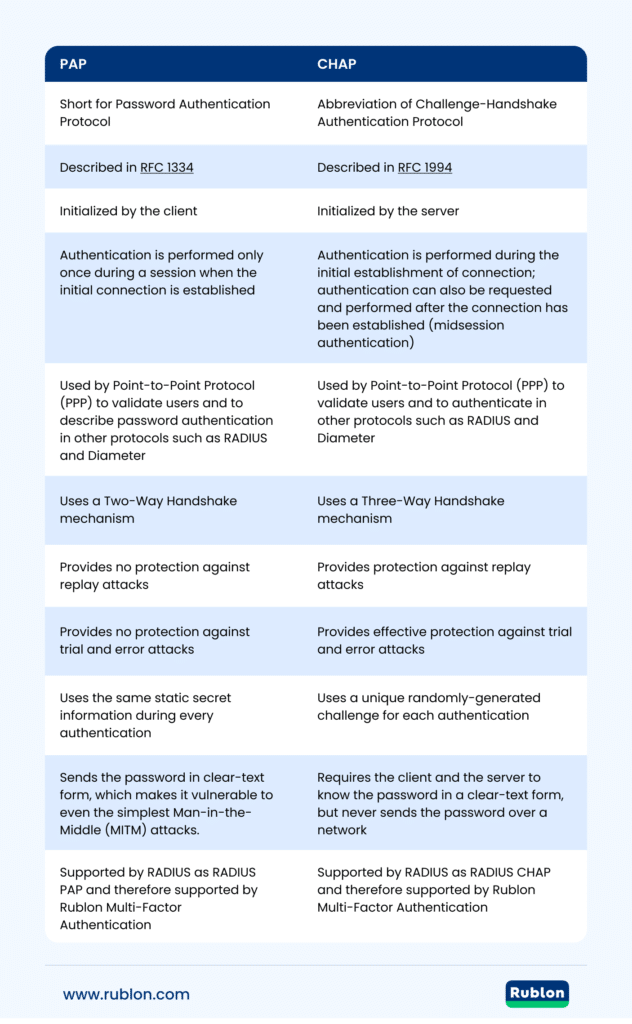
| PAP | CHAP |
| Short for Password Authentication Protocol | Abbreviation of Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol |
| Described in RFC 1334 | Described in RFC 1994 |
| Initialized by the client | Initialized by the server |
| Authentication is performed only once during a session when the initial connection is established | Authentication is performed during the initial establishment of connection; authentication can also be requested and performed after the connection has been established (midsession authentication) |
| Used by Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to validate users and to describe password authentication in other protocols such as RADIUS and Diameter | Used by Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to validate users and to authenticate in other protocols such as RADIUS and Diameter |
| Uses a Two-Way Handshake mechanism | Uses a Three-Way Handshake mechanism |
| Provides no protection against replay attacks | Provides protection against replay attacks |
| Provides no protection against trial and error attacks | Provides effective protection against trial and error attacks |
| Uses the same static secret information during every authentication | Uses a unique randomly-generated challenge for each authentication |
| Sends the password in clear-text form, which makes it vulnerable to even the simplest Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks | Requires the client and the server to know the password in a clear-text form but never sends the password over a network |
| Supported by RADIUS as RADIUS PAP and therefore supported by Rublon Multi-Factor Authentication | Supported by RADIUS as RADIUS CHAP and therefore supported by Rublon Multi-Factor Authentication |
What Are the Advantages of PAP Over CHAP?
- The only advantage of PAP over CHAP is that PAP is compatible with all network operating systems, so extremely simple or very old systems that do not support CHAP can still use PAP for authentication
What Are the Advantages of CHAP Over PAP?
- CHAP does not send the password over a network, while PAP transfers the password between the parties and therefore proves extremely vulnerable to eavesdropping-based attacks
- In contrast to PAP, CHAP sends authentication challenges at regular intervals to ensure the client has not been compromised or replaced with a malicious actor
Get started by signing up for a Free 30-Day Rublon Trial →