Last updated on February 10, 2026
Global Policy vs. Application Policy vs. Group Policy
Effective Policy Order
- Group Policy – Overrides the settings of Application Policy and Global Policy
- Application Policy – Overrides the settings of Global Policy
- Global Policy – These settings are applicable only if not overridden by Group Policy or Application Policy
If several group policies refer to the group to which a user belongs, the order of these group policies is the deciding factor. Using the Move To Top option, you can change the order of policies when editing an application.
However, the Geolocation Policy is a special case. When evaluating behavior, the system uses an internal rule‑type priority (described in detail in Geolocation Policy). In practice, this means that:
- Geolocation can take precedence over other rule types (e.g., Authorized Networks, Remembered Devices) even if they are defined in a higher‑precedence policy.
- For example, Geolocation defined in an Application Policy is still applied over Authorized Networks defined in a Group Policy, due to the internal evaluation order of rule types.
Policy Order Example

Common Group Policy Use Cases
Disable Remembered Devices for IT Admins
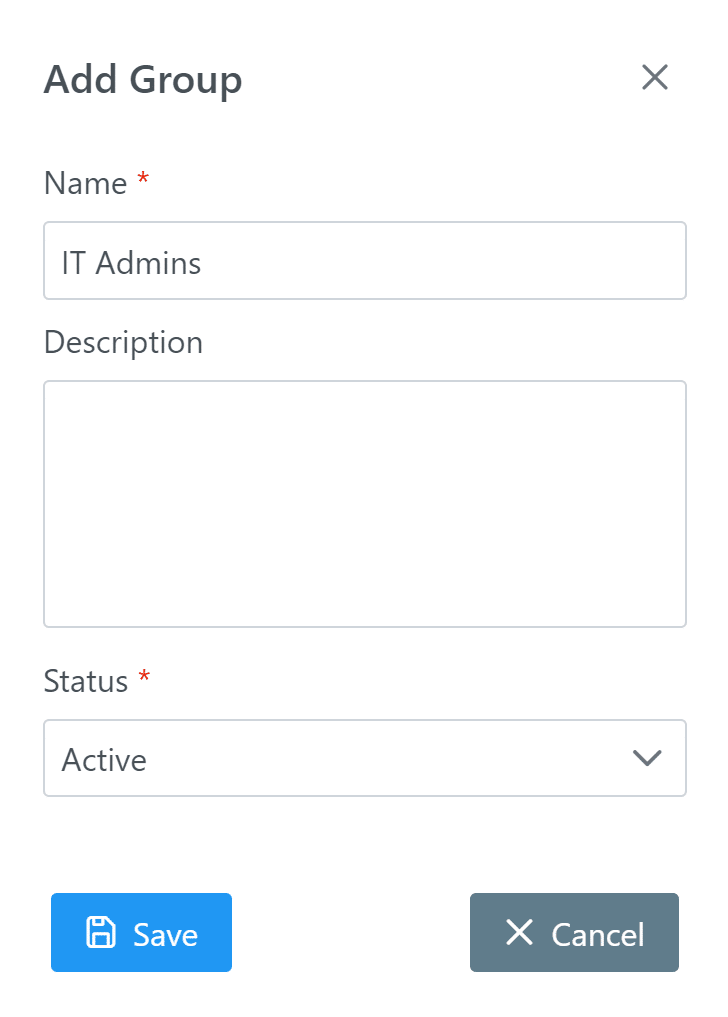
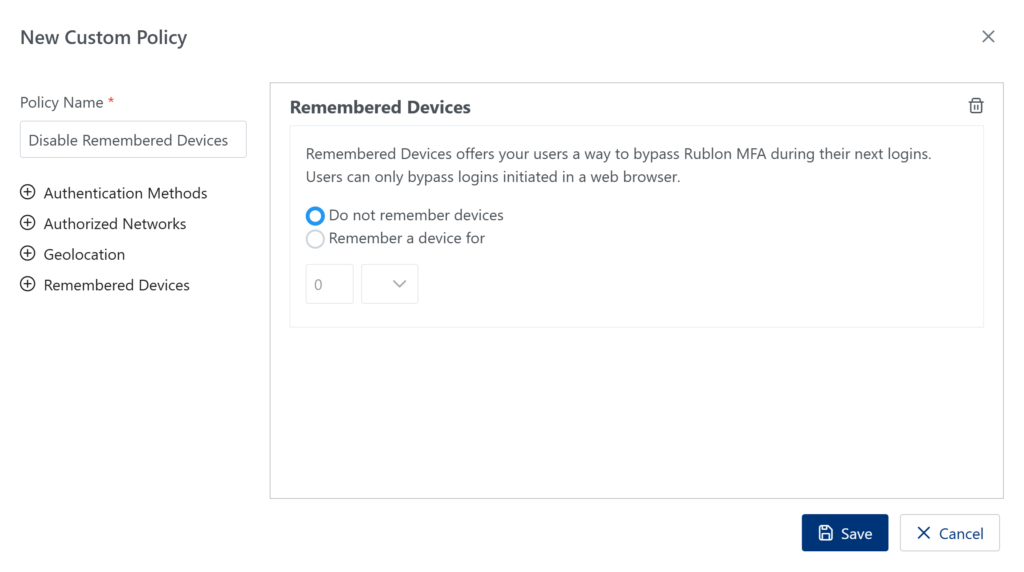
Require IT Admins to use hardware keys
Disable the SMS Passcode authentication method for external users
1. Sign in to the Rublon Admin Console.
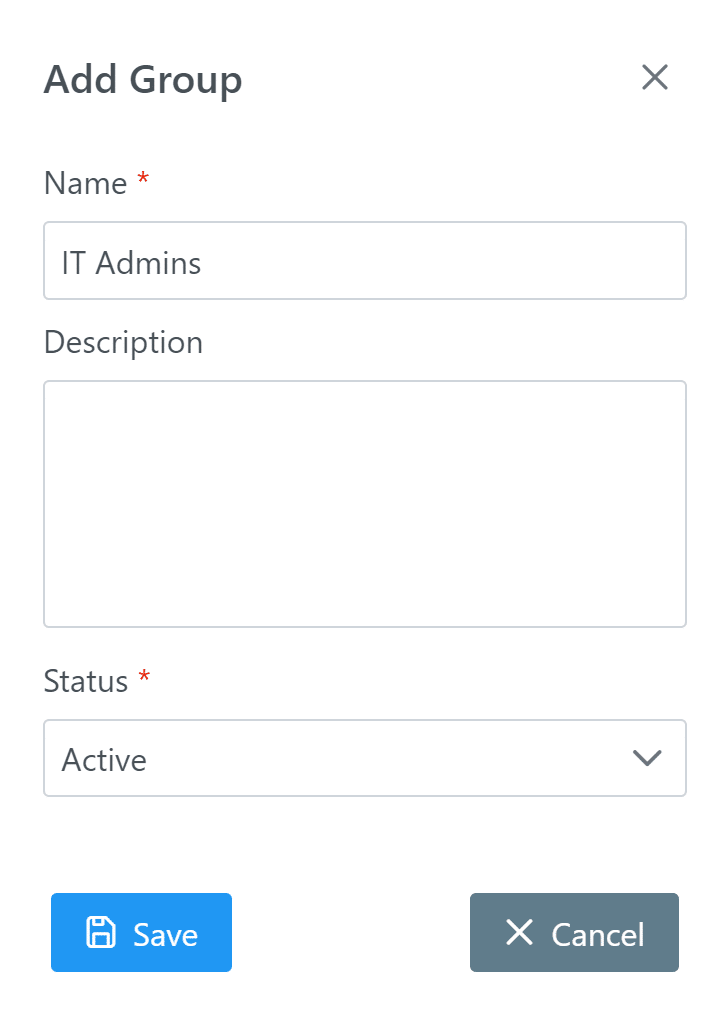
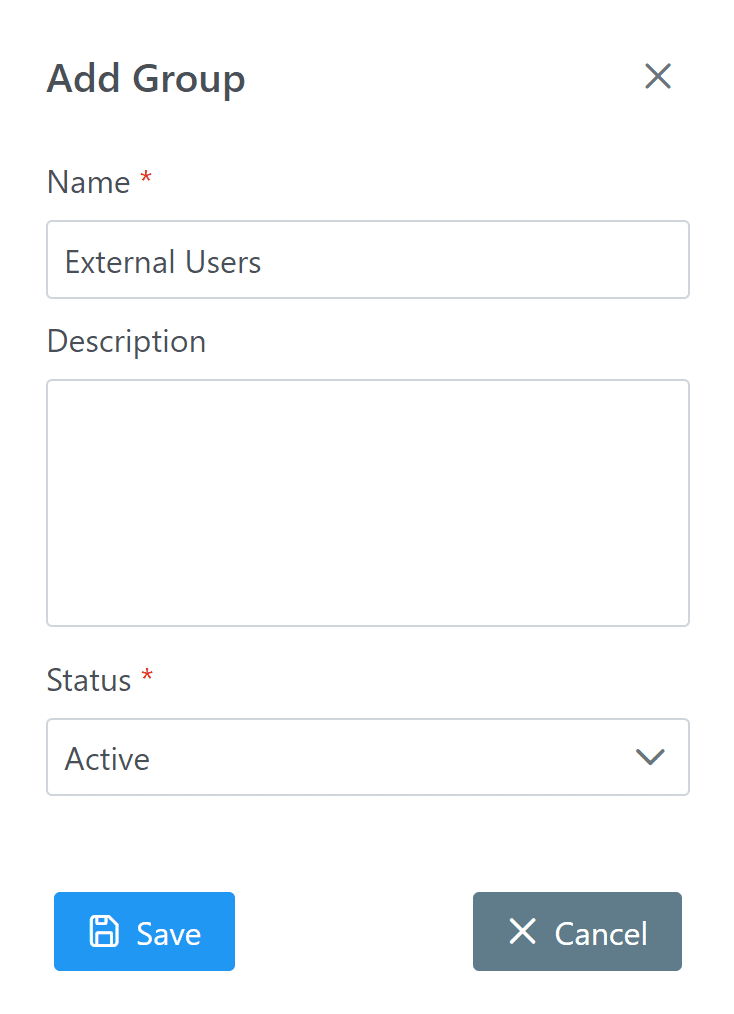
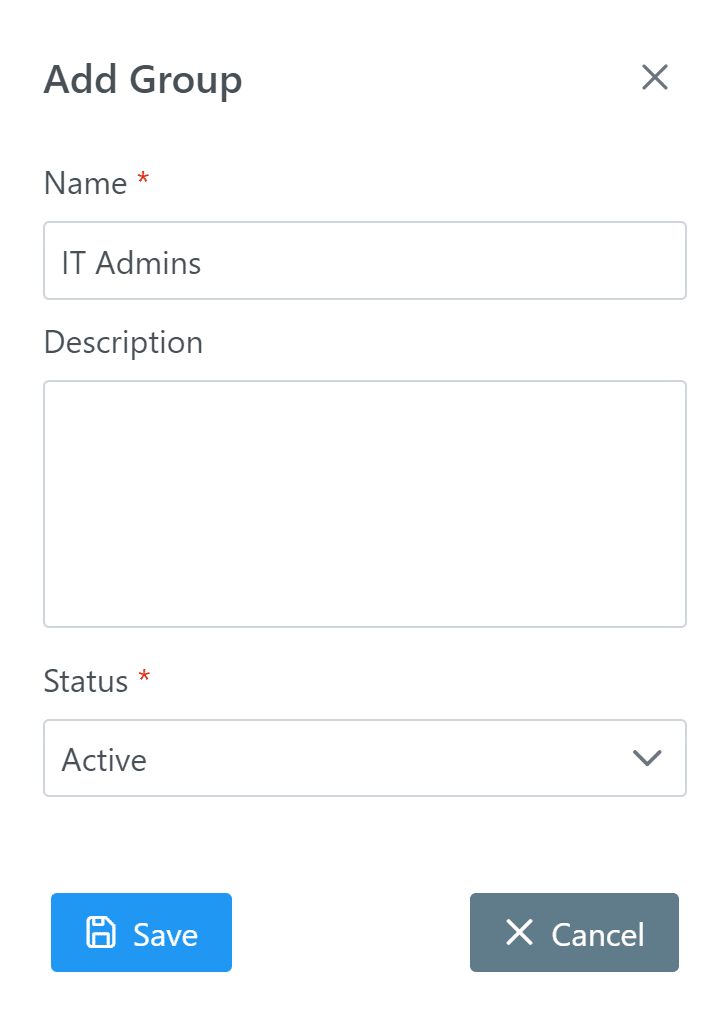
2. In the Groups tab, create an External Users user group. (See: How to add group)
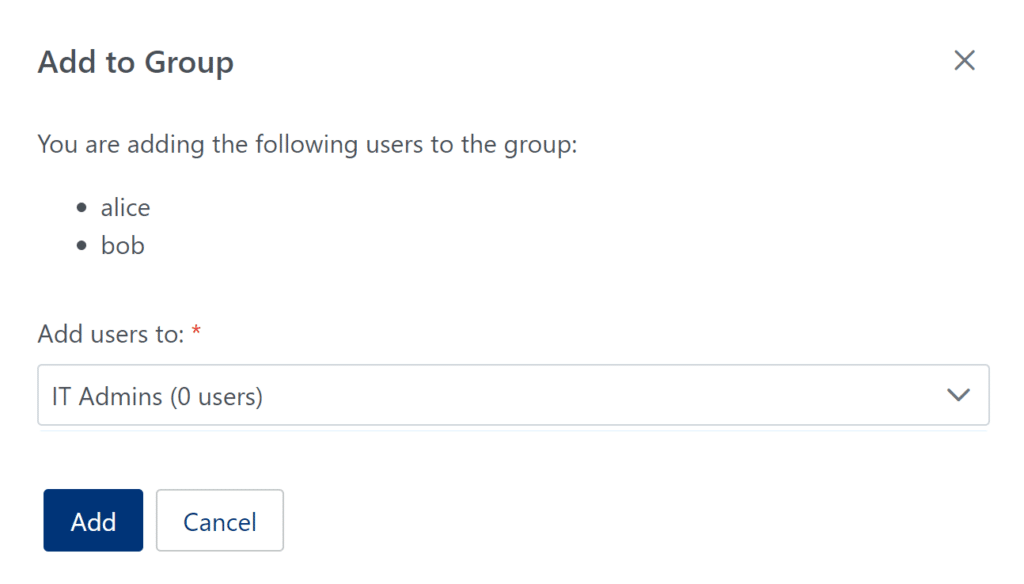
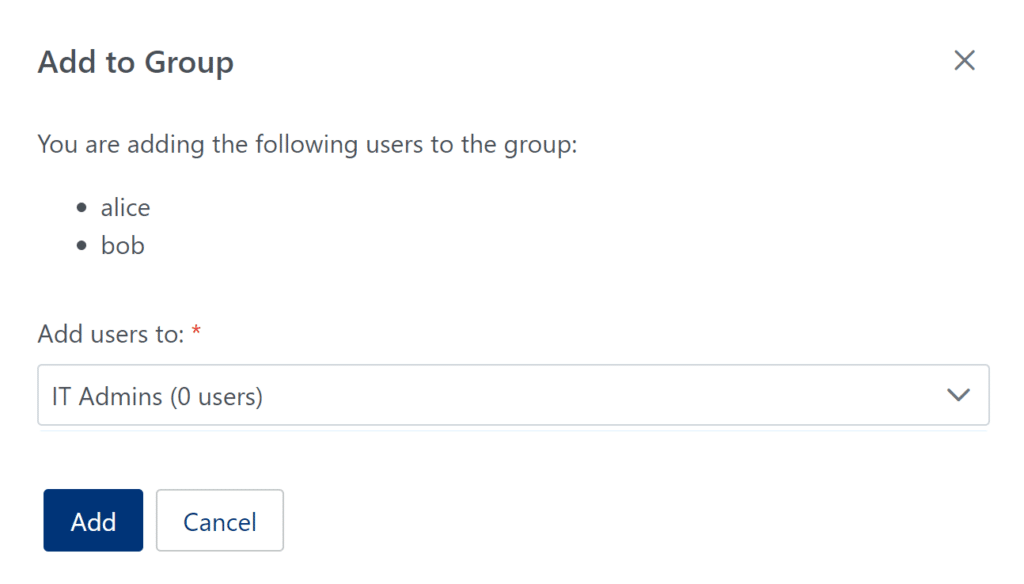
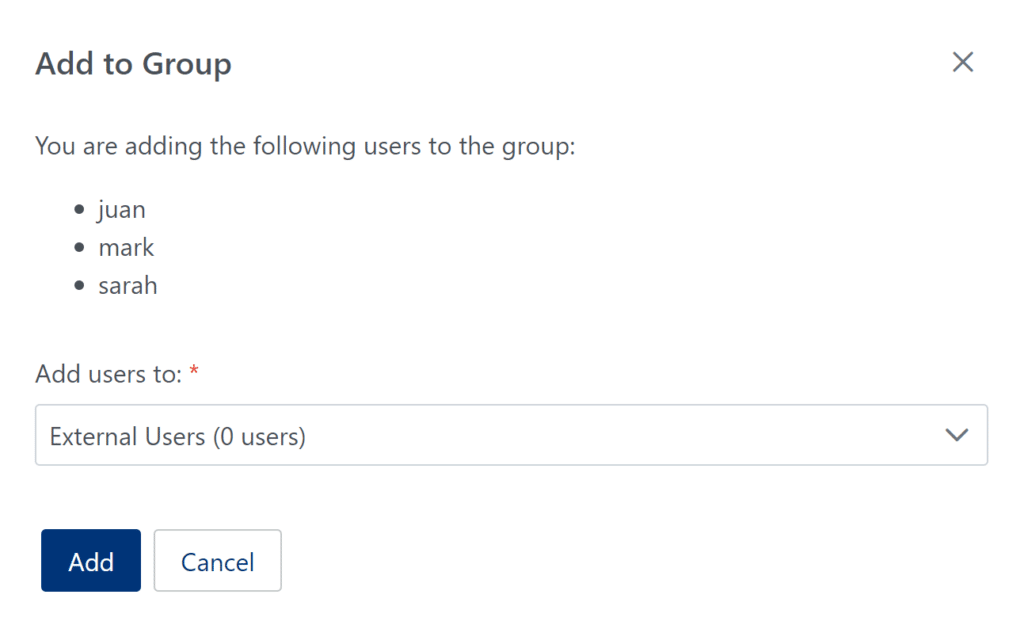
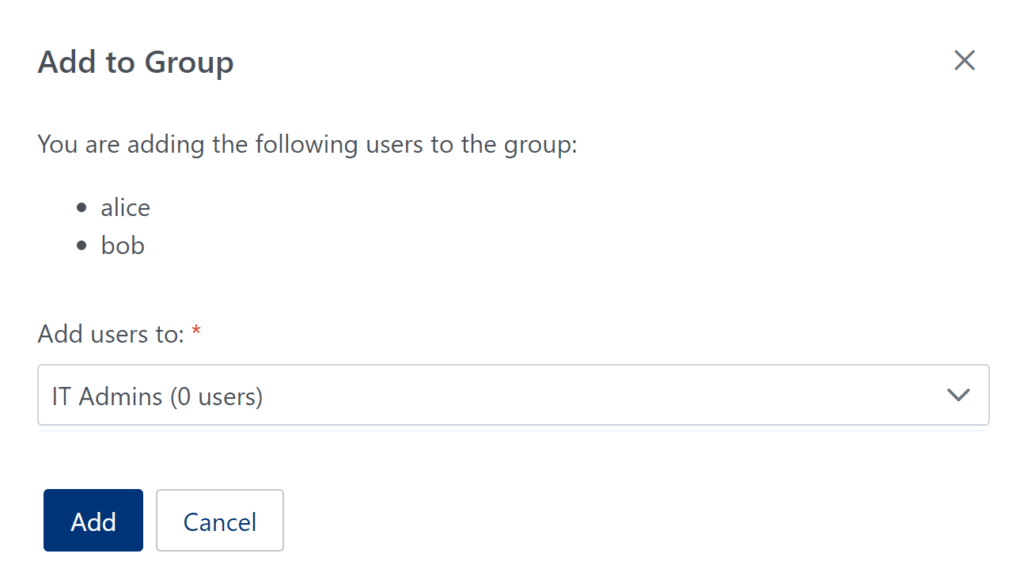
3. In the Users tab, add the external users in your organization to the External Users group. (See: How to add users to group)
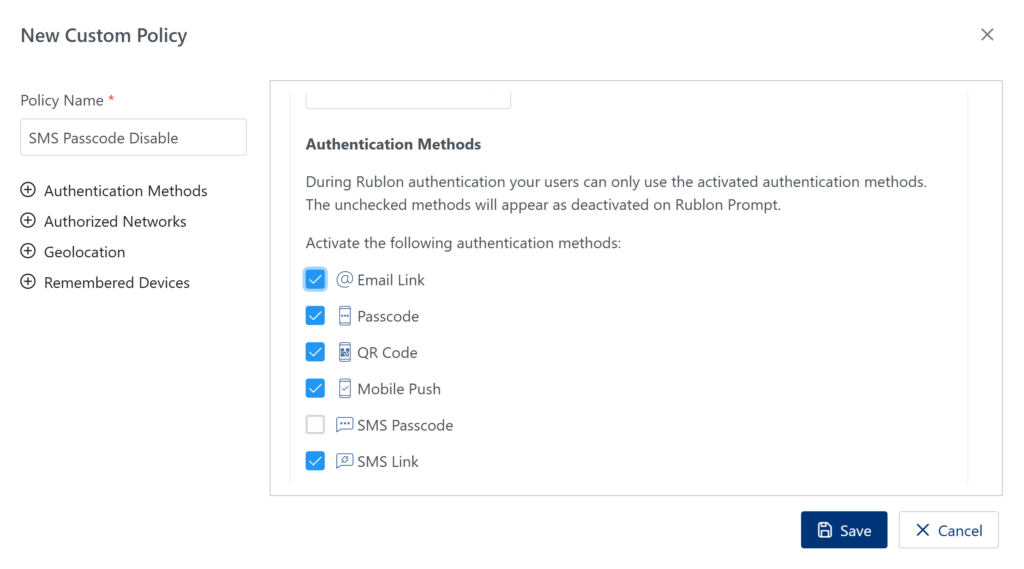
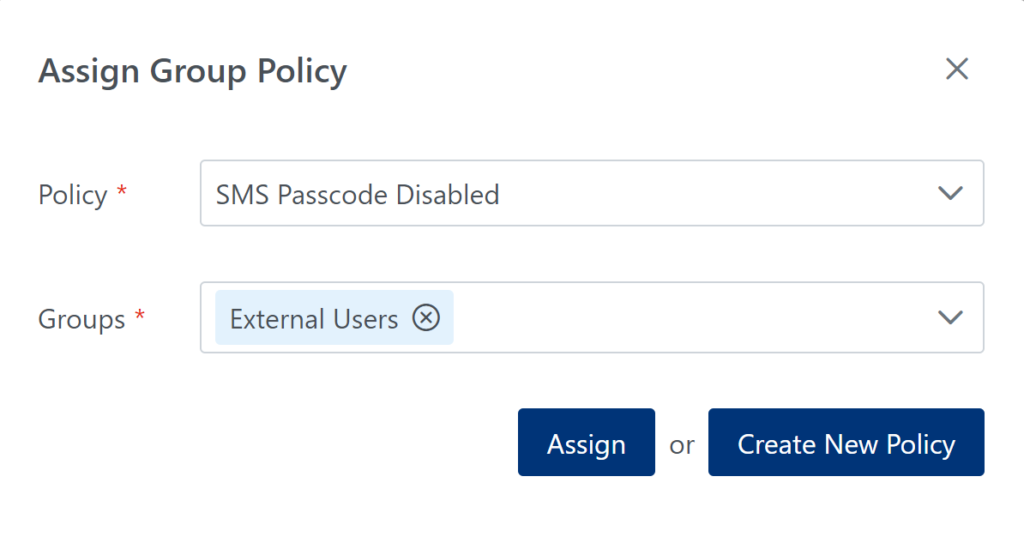
Bypass MFA for local network access for regular users but not IT Admins
Assumptions
Steps
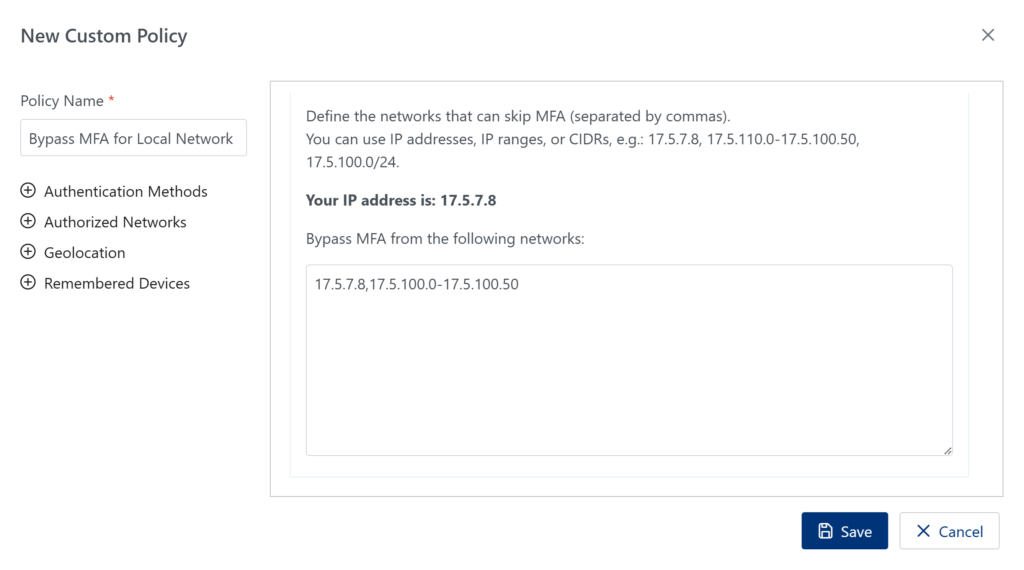
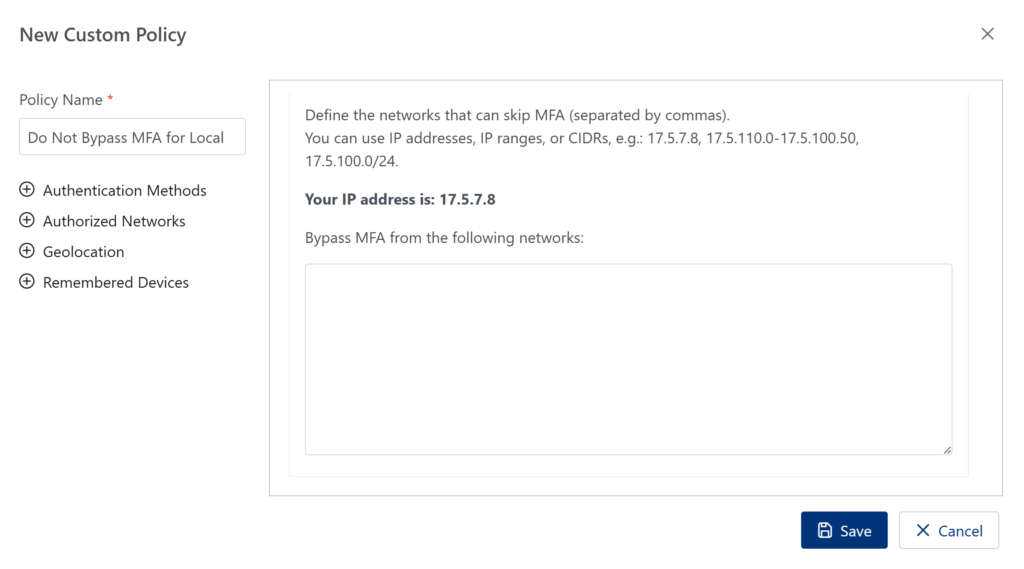
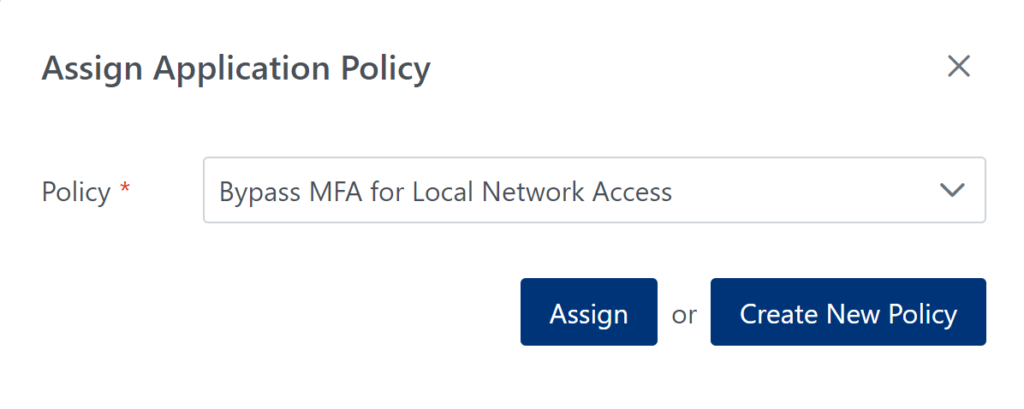
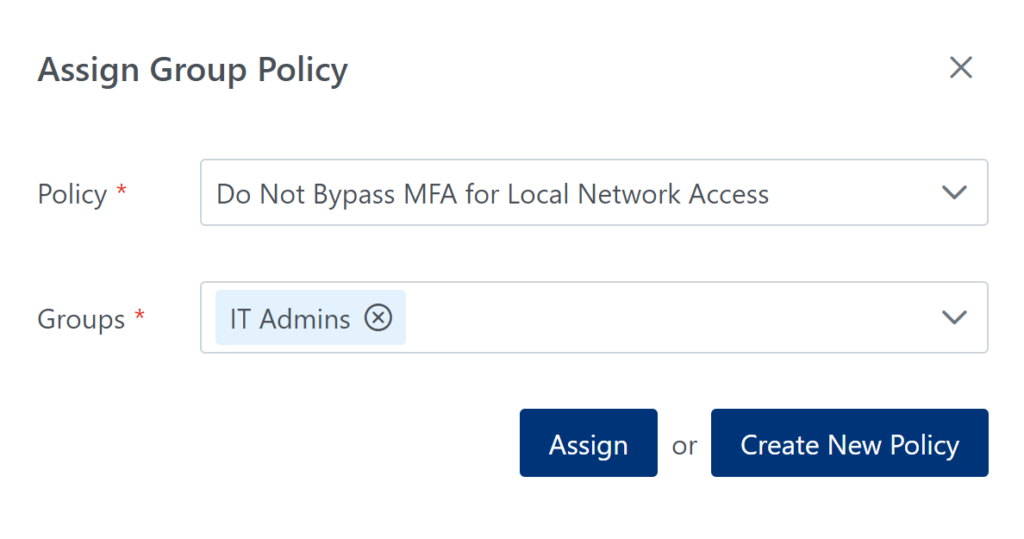
Result
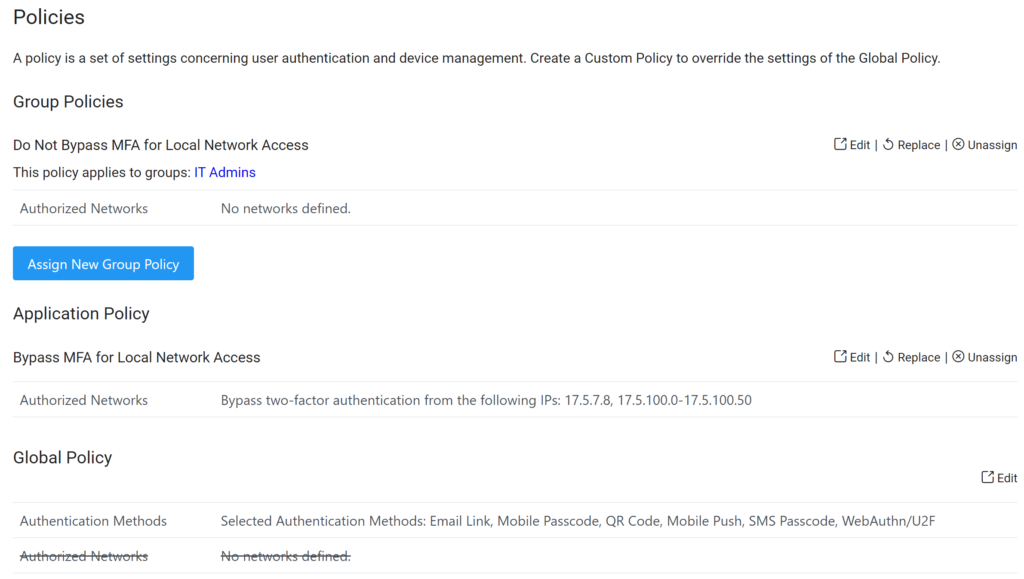
Apply advanced geolocation controls only to the IT Admins group
Assumptions
An organization wants to apply different authentication rules based on the user’s geographical location, but only for a specific group, such as the organization’s IT Administrators. Users in this group should:
- bypass MFA when signing in from trusted countries,
- be required to complete MFA when signing in from all other countries,
- and be fully denied access when signing in from two high‑risk countries
Other users in the organization should not be affected by this policy since it only applies to that specific user group.
Steps
1. Sign in to the Rublon Admin Console.
2. In the Groups tab, create an IT Admins user group. (See: How to add group)
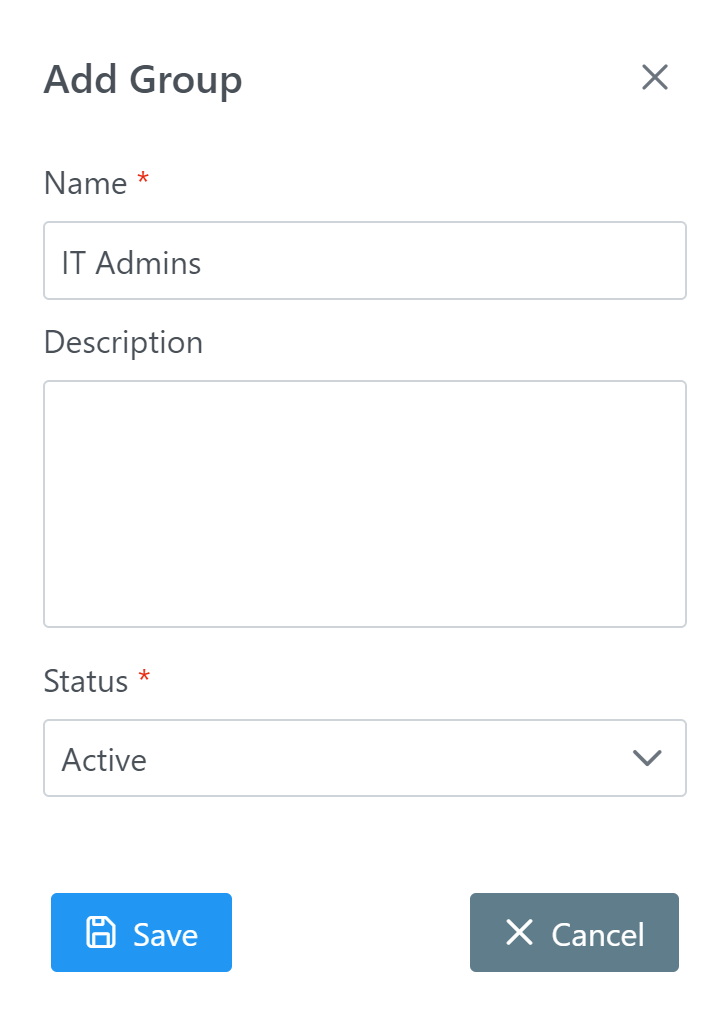
3. In the Users tab, add the IT Admins in your organization to the IT Admins group. (See: How to add users to group)
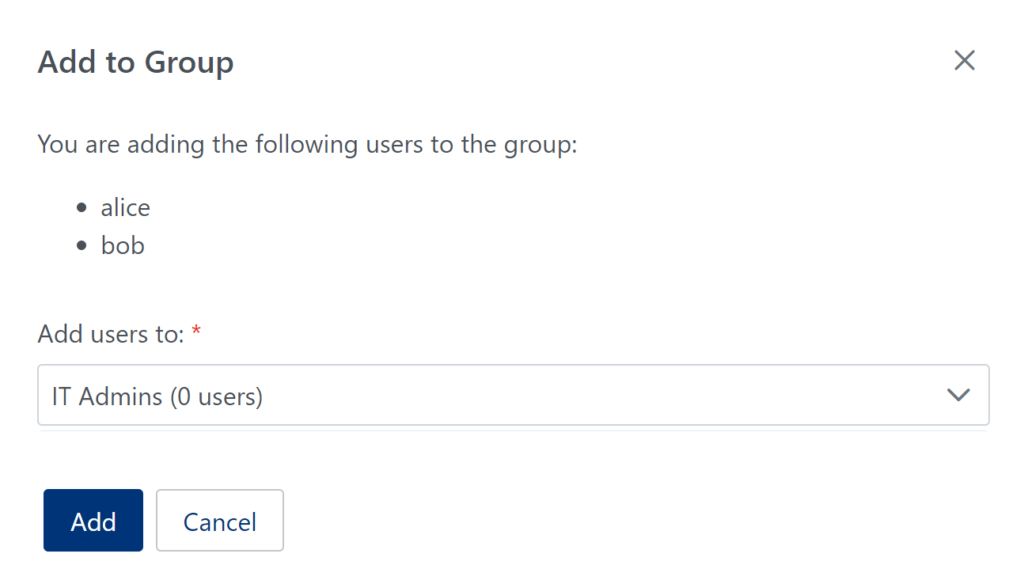
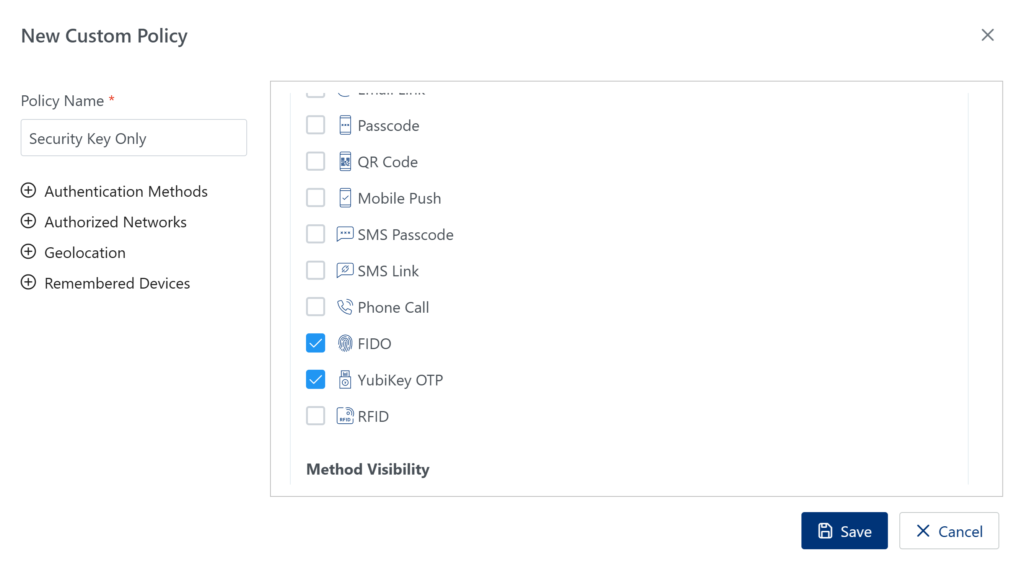
4. In the Policies tab, create an IT Admins Geolocation policy where you enable the following settings:
- Bypass MFA: select trusted countries,
- Enforce MFA: select all remaining countries,
- Deny Access: select one or two high‑risk countries.
(See: How to create new policy and Authorized Networks)
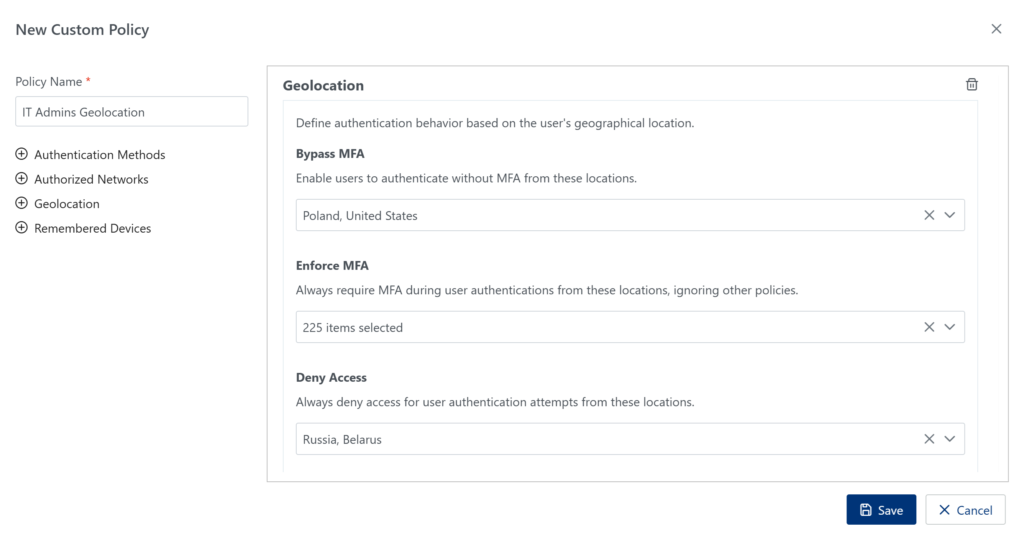
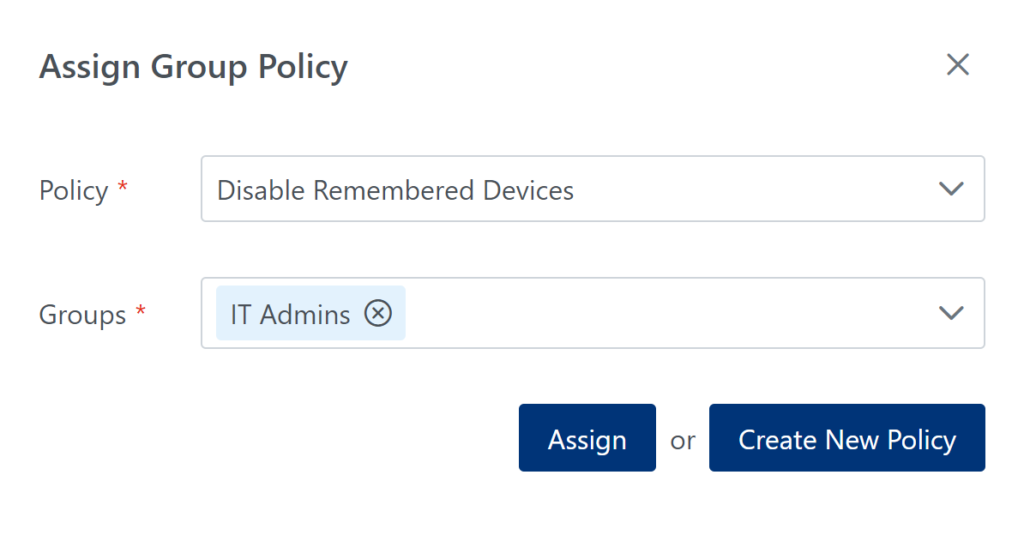
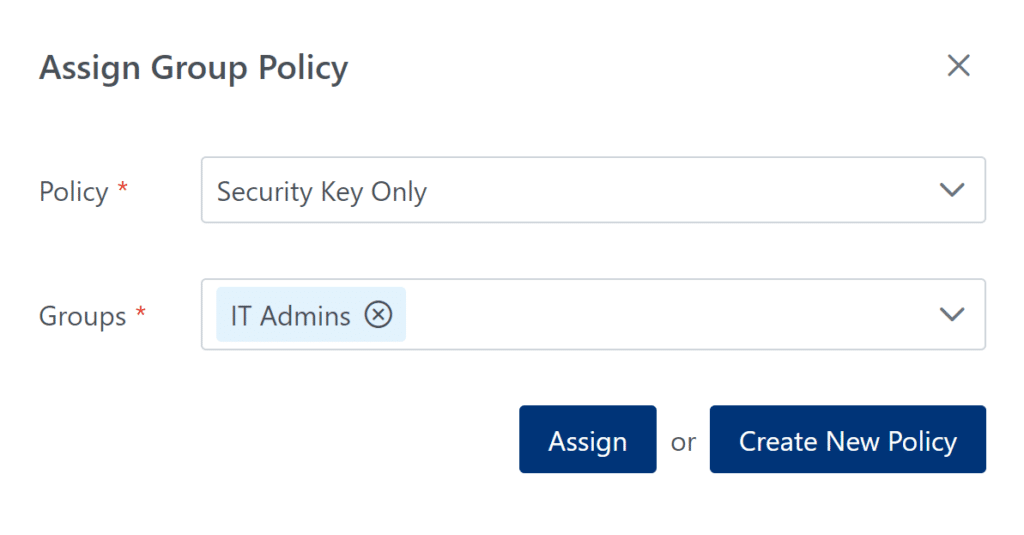
5. In the Applications tab, assign the IT Admins Geolocation policy as a Group Policy to the IT Admins group in one or more applications. (See: How to assign Group Policies to groups within application)
Result
Geolocation rules apply only to a specific group of IT Admins, not the entire organization, which results in:
- Reduced MFA friction for trusted‑location logins within the selected group.
- Stronger security for group members signing in from unknown or less-trusted regions.
- Complete protection from high‑risk countries through full access denial.
- Centralized management of complex geolocation rules in a single Group Policy.