Last updated on July 29, 2025
Key ENISA NIS2 MFA Requirements
- MFA or Continuous Authentication – § 11.7.1: critical assets must be protected by multiple factors or a risk‑based continuous‑auth mechanism.
- Strength Matches Asset Sensitivity – § 11.7.2: choose methods whose assurance level corresponds to the data/system classification; phishing‑resistant options (FIDO2 security keys & passkeys) are recommended “wherever possible”.
- Privileged & Administrative Accounts – § 11.3.2(a–d): use dedicated, individual admin accounts secured with strong authentication and limited privileges.
- System‑Administration Networks – § 11.4: access must be tightly controlled and fully logged; MFA is strongly advised for these systems.
- Remote & Internet‑Facing Access – Guidance: always enforce MFA on VPN, RDP, e‑mail portals, and any service exposed to the Internet or accessed from outside the corporate network.
- Evidence & Periodic Review – § 11.6.4: keep authentication logs, document risk analysis, and review MFA procedures at planned intervals (ENISA suggests every ≤ two years).
ENISA Guidance: When Should Entities Deploy MFA?

1. MFA for Privileged Accounts and System Administration Accounts
ENISA Requirement:
"11.3 PRIVILEGED ACCOUNTS AND SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION ACCOUNTS
11.3.1. The relevant entities shall maintain policies for management of privileged accounts and system administration accounts as part of the access control policy referred to in point 11.1.
11.3.2. The policies referred to in point 11.3.1. shall:
(a) establish strong identification, authentication such as multi-factor authentication and authorisation procedures for privileged accounts and system administration accounts;
(b) set up specific accounts to be used for system administration operations exclusively, such as installation, configuration, management or maintenance;
(c) individualise and restrict system administration privileges to the highest extent possible,
(d) provide that system administration accounts are only used to connect to system administration systems."Why This Matters?
How Rublon MFA Satisfies This Requirement
2. MFA for Administration Systems
ENISA Requirement:
"11.4 ADMINISTRATION SYSTEMS
11.4.1. The relevant entities shall restrict and control the use of system administration systems in accordance with the access control policy referred to in point 11.1."
"Require strong authentication mechanisms such as MFA for accessing system administration systems."Why This Matters?
How Rublon MFA Satisfies This Requirement
Looking for FIDO MFA Provider?
Protect Active Directory and Entra ID users from hackers with phishing-resistant FIDO security keys and passkeys.
3. MFA for Secure Authentication
ENISA Requirement:
"11.6 AUTHENTICATION
11.6.1. The relevant entities shall implement secure authentication procedures and technologies based on access restrictions and the policy on access control."In addition, ENISA recommends the use of phishing-resistant MFA, pointing out that this “strong” type of authentication uses no shared secrets and is not vulnerable to an attacker-in-the-middle attack. A protected cryptographic private key can be securely registered with a domain, in accordance with Fast Identity Online (FIDO) and W3C WebAuthn standards, or a trust provider, following public key infrastructure and International Telecommunication Union X.509 standards.
Why This Matters?
How Rublon MFA Satisfies This Requirement
✅ Strong Phishing-Resistant Authenticators: Rublon MFA supports FIDO2 & FIDO U2F security keys like YubiKey and Google Titan, as well as software and hardware passkeys compatible with FIDO standards, enabling true phishing resistance.
4. MFA for Accessing Network and Information Systems
ENISA Requirement:
"11.7 MULTI-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION
11.7.1. The relevant entities shall ensure that users are authenticated by multiple authentication factors or continuous authentication mechanisms for accessing the entities’ network and information systems, where appropriate, in accordance with the classification of the asset to be accessed.
11.7.2. The relevant entities shall ensure that the strength of authentication is appropriate for the classification of the
asset to be accessed."Why This Matters?
How Rublon MFA Satisfies This Requirement

✅ Secure Fallback Methods: Administrators can issue time‑bound Bypass Codes or switch a user to an alternate factor (e.g., push) when a primary authenticator is unavailable; all such events are logged, satisfying ENISA’s call for “secure fallback methods”.
✅ Policy-Based Access Control: Rublon MFA enables entities to enforce different authentication strengths depending on the asset’s classification. High-risk systems can require stronger MFA methods, ensuring compliance with ENISA’s requirement to match authentication strength to asset sensitivity.
✅ Seamless Integration with Systems: Rublon MFA integrates with VPNs, remote access software, and email clients like Outlook Web App (OWA) or Roundcube. It supports protocols like LDAP, RADIUS, and SAML, enabling robust MFA enforcement across all access points.

Important Considerations for Achieving NIS2 Directive Compliance
1. Training Users on Multi-Factor Authentication
ENISA Requirement:
"Educate users about the importance of MFA and how to use it."Why This Matters?
How Rublon MFA Supports This Initiative
2. Alignment with Other Standards and Frameworks
Why This Matters?
How Rublon MFA Facilitates Compliance Across Frameworks
Subscribe to the Rublon Newsletter
Top Tips for Implementing MFA for NIS2 Compliance
1. Integrate MFA with SSO
2. Provide Secure Fallback Methods
3. Educate Users About MFA
4. Monitor MFA Logs Regularly
5. Keep MFA Systems Updated
Get started by signing up for a Free 30-Day Rublon Trial →
6. Implement Contextual MFA
7. Evaluate MFA Providers Carefully
8. Pilot Test the MFA Solution
9. Ensure Legal Compliance
How Rublon MFA Satisfies ENISA’s NIS2 MFA Guidance
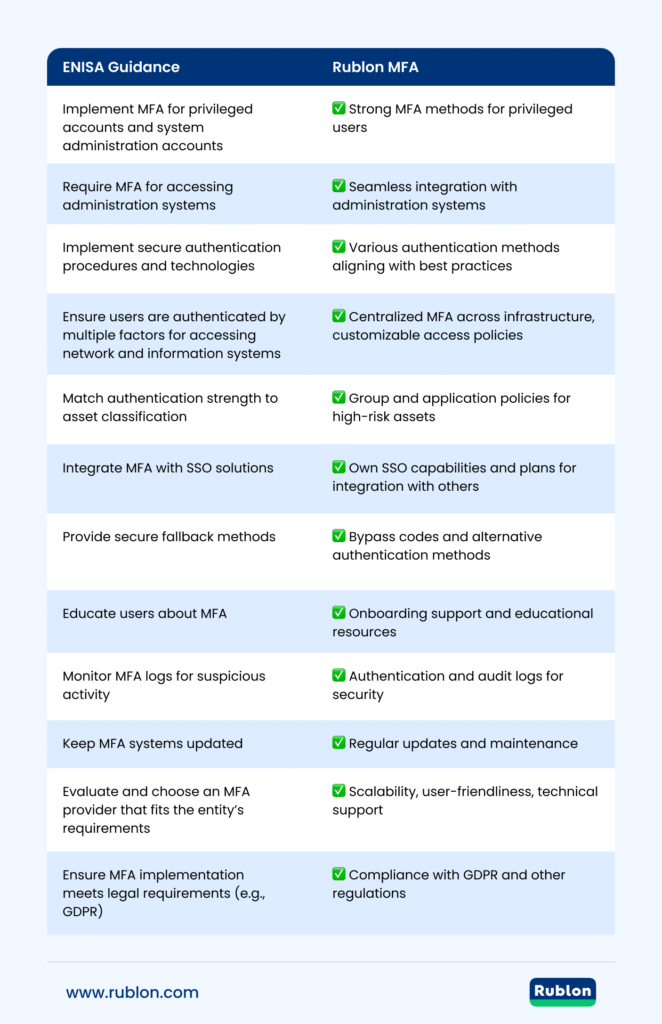
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions on ENISA NIS2 MFA Guidance
Do ENISA’s NIS2 guidelines mandate MFA on every login?
No. Each organization must decide when to require MFA (e.g., on every login, once per session, or only for high‑risk actions). However, it remains a security best practice to enforce MFA on every login.
What are examples of “phishing‑resistant MFA”?
FIDO U2F & FIDO2 hardware security keys and passkeys, smart cards with cryptographic certificates, and built‑in device authenticators (e.g., biometric keys). SMS codes and push notifications are not considered phishing‑resistant.
Are push notifications still acceptable?
Yes. ENISA classifies push notifications as medium‑strength MFA but does not prohibit them.
How often should MFA policies be reviewed?
ENISA recommends reviewing them “at planned intervals,” after any significant change or incident, and at least once every two years.
Are shared admin accounts prohibited?
They should be avoided unless absolutely necessary (§ 11.5.3). If used, they must be formally justified, explicitly approved, documented, secured with MFA, and subject to least‑privilege controls.
